
The History of DLSS
DLSS 1.0 (2018)
Ray Tracing
In 2018, NVIDIA rebranded their GeForce GTX gaming graphics cards to GeForce RTX graphics cards. This change was to coincide with the upcoming ray tracing technology, which simulated the bounces of rays of light but came with a massive performance cost.
Initial Model
DLSS 1.0 was NVIDIA's first attempt at using deep learning to upscale lower-resolution images to higher resolutions. Launched with the RTX 20-series GPUs in 2018, it aimed to offset the performance cost of ray tracing by rendering at a lower resolution and then using AI to upscale the image.
- Required per-game training on NVIDIA's supercomputers
- Often resulted in blurry images compared to native resolution
- Available in only a handful of games initially
- Only compatible with the latest generation of GPUs
Technical Approach
DLSS used a convolutional autoencoder to compare lower resolution images with ultra high resolution 16k images. The model was trained on a per-game basis, limiting the number of games at launch.
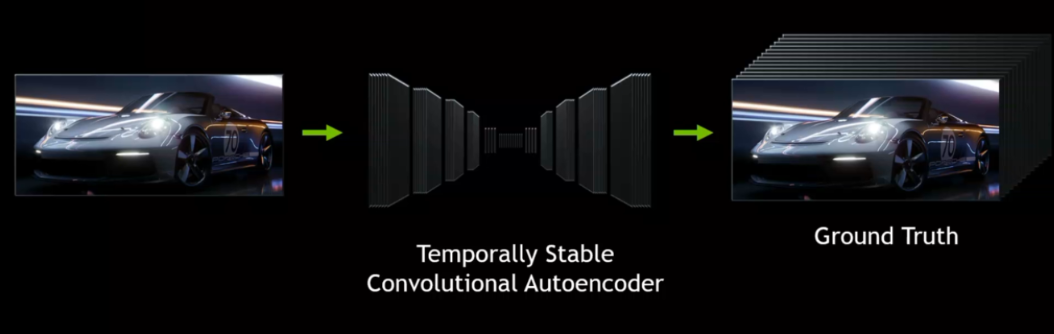

DLSS 2
Major Improvements
DLSS 2 (2020)
Improvements
Released in 2020, DLSS 2 showed enhancements over the previous version in several ways. It allowed many more games to feature the technology and had visual improvements compared to its previous version. Due to its strong upscaling capabilities and availability across many games, DLSS ballooned in popularity in the early 2020s.
- No longer required per-game training
- Used game engine motion vectors for increased accuracy
- Wider game support
- Available on more graphics cards


DLSS 3
Frame Generation Introduced
DLSS 3 (2022)
Frame Generation
Launched with the RTX 40-series GPUs in 2022, DLSS 3 added a new technology: AI-powered frame generation, nearly doubling frame rates.
- Used Optical Flow Accelerator hardware in RTX 40-series GPUs
- Could double frame rates in some cases
- Exclusive to RTX 40-series GPUs
Limitations and Controversies
While DLSS 3 frame generation significantly boosted frame rates, it introduced additional latency and could sometimes produce visual artifacts. NVIDIA claimed a doubling in performance, but generated frames don't respond to player input; instead, they increase the motion fluidity. Despite these criticisms, DLSS 3 has been widely adopted in modern AAA games.
DLSS 4
The Transformer
DLSS 4 (2025)
The Latest Model
Released in early 2025 with the 50-series GPUs, DLSS 4 showed the biggest jump in technology since version 2 in 2020. NVIDIA announced multi frame generation (MFG), an enhanced model for the older frame generation, and a new transformer-based upscaling model.
- MFG allowed 50-series GPUs to generate up to 3 frames for every 1 rendered frame
- Enhanced frame generation for 40-series GPUs reduced memory usage and increased visual fidelity
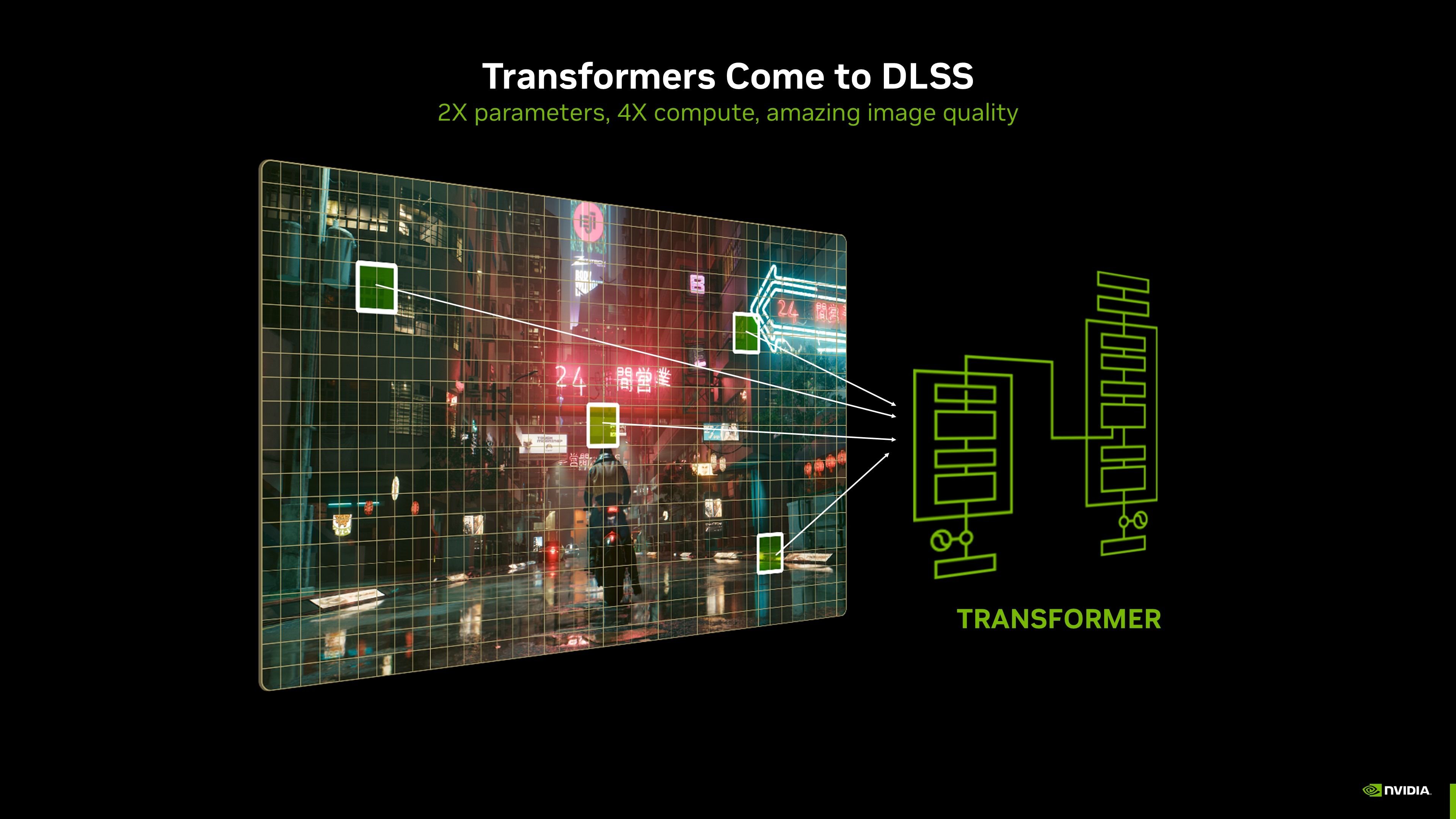
- Transformer model for all RTX cards (20-series and newer) drastically increased quality of upscaling
- Better handling of fine details like hair and foliage, especially in motion
CNN vs Transformer Model Comparison
Previous CNN Model
Convolutional Neural Networks work well processing patches of information but struggle with understanding relationships between distant parts of an image, causing details to be lost.

New Transformer Model
The transformer architecture understands relationships between all pixels in an image, significantly improving visual detail, especially in motion.

The above images show a zoomed in shot of a backpack while in motion with the old CNN model and the new transformer model.
NVIDIA's Performance Claims
NVIDIA has claimed that 50-series GPUs significantly outperform older generation cards. However, NVIDIA's metric for performance is frames per second, rather than total compute power. This led to the statement that the 5070, a midrange card, had the same performance as the 4090, the previous generation's flagship card. This was because the 5070 allowed for multi frame generation, so while the 5070 could technically reach the same frame rate as the 4090, it had worse input latency and visual artifacts.

Future Implications
DLSS has shown massive improvements over the last half decade, significantly improving performance for only a small decrease in quality. While there are several valid criticisms of NVIDIA's DLSS, such as reductions in visual fidelity and increasing latency with frame generation, this rapid improvement in technology has allowed many gamers to keep their older graphics cards for longer and use upscaling instead. A concern for many, though, is that game studios will use DLSS and frame generation as a crutch for the lack of game optimization, decreasing game quality overall. However, having DLSS and other upscaling technology as an option to use will always be a benefit to gamers.